* 이 글은 Return Oriented Programming (ROP) 에서 이어지는 글입니다.
* 컴파일 command line: gcc test.c -o test -m32 -Wl,-z,relro -no-pie -fno-pie -fno-stack-protector -mmanual-endbr -O0 -ggdb
Last update: 6/25/2020
cdecl
x86에서 함수는 일반적으로 cdecl 호출 규약을 따른다. 각 인자는 push 명령어로 stack에 저장되며, caller가 stack을 정리한다.
다음 예시를 살펴보자.
|
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
int function1(int x) {
return 1; } int function2(int x, int y) { return 2; } int function3(int x, int y, int z) { return 3; } int function4(int x, int y, int z, int w) { return 4; } int main() { function1(1); function2(0x11, 0x12); function3(0x21, 0x22, 0x23); function4(0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34); return 0; } |
|
gdb-peda$ pd main
Dump of assembler code for function main: 0x0804919e <+0>: push ebp 0x0804919f <+1>: mov ebp,esp 0x080491a1 <+3>: push 0x1 0x080491a3 <+5>: call 0x8049176 <function1> 0x080491a8 <+10>: add esp,0x4 0x080491ab <+13>: push 0x12 0x080491ad <+15>: push 0x11 0x080491af <+17>: call 0x8049180 <function2> 0x080491b4 <+22>: add esp,0x8 0x080491b7 <+25>: push 0x23 0x080491b9 <+27>: push 0x22 0x080491bb <+29>: push 0x21 0x080491bd <+31>: call 0x804918a <function3> 0x080491c2 <+36>: add esp,0xc 0x080491c5 <+39>: push 0x34 0x080491c7 <+41>: push 0x33 0x080491c9 <+43>: push 0x32 0x080491cb <+45>: push 0x31 0x080491cd <+47>: call 0x8049194 <function4> 0x080491d2 <+52>: add esp,0x10 0x080491d5 <+55>: mov eax,0x0 0x080491da <+60>: leave 0x080491db <+61>: ret End of assembler dump. |
call 실행 이후 esp를 증가시킨다.
최적화 옵션을 끈 상태에서 컴파일하면, 함수는 인자에 접근하기 위해 ebp 레지스터를 사용한다. (최적화 옵션을 키면 esp를 사용한다)
다음 예시로 이 사실을 확인할 수 있다. ebp+0 은 SFP를 가리키며, ebp+4는 RET이다.
|
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
int add(int x, int y) {
return x+y; } int main() { add(1, 2); return 0; } |
|
gdb-peda$ pd add
Dump of assembler code for function add: 0x08049176 <+0>: push ebp 0x08049177 <+1>: mov ebp,esp 0x08049179 <+3>: mov edx,DWORD PTR [ebp+0x8] 0x0804917c <+6>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp+0xc] 0x0804917f <+9>: add eax,edx 0x08049181 <+11>: pop ebp 0x08049182 <+12>: ret End of assembler dump. |
ROP 32bit :: Basic
ROP로 함수를 1개 호출하는 과정을 살펴보자.
최적화 옵션을 끄면 함수가 인자에 접근하기 위한 기준으로 ebp가 사용된다. 함수 프롤로그 push ebp ; mov ebp, esp 으로 ebp가 기존의 esp가 되기 때문에, 아래처럼 payload를 구성해서 인자를 전달할 수 있다.
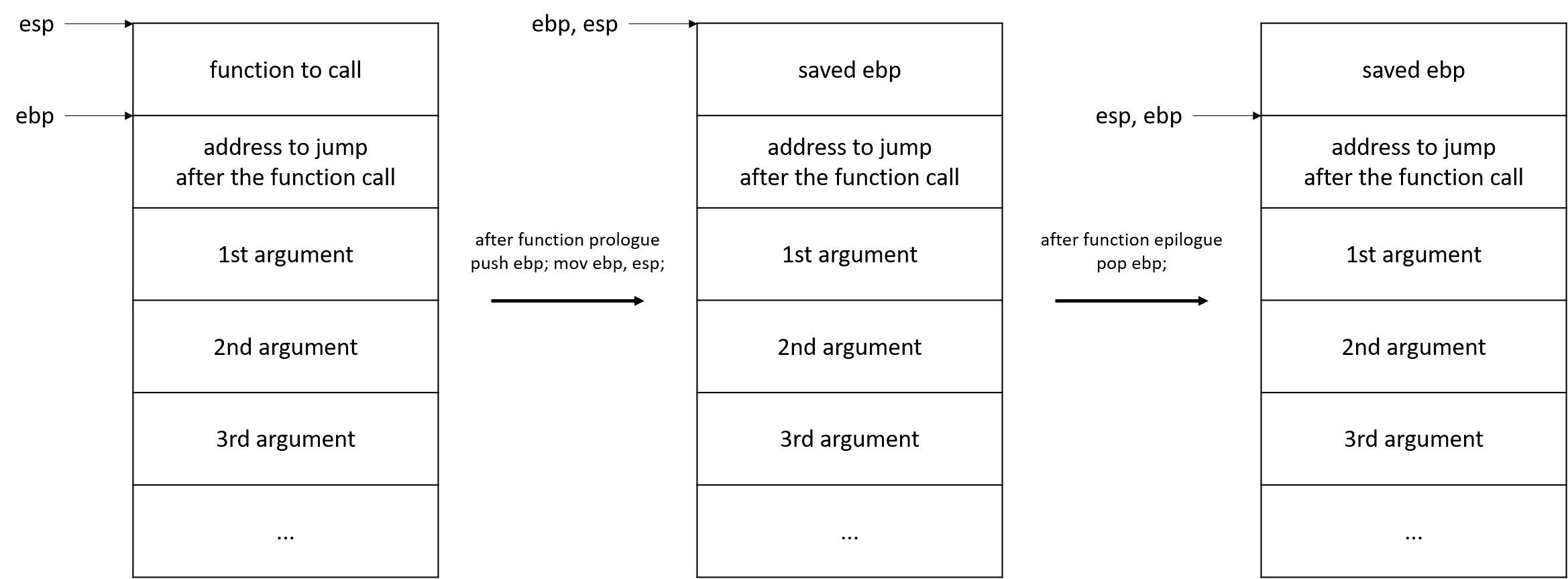
아래 코드는 ROP로 write를 사용해 문자열을 출력한다.
|
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h> char *buf = "Hello ROP\n"; void function() { uint32_t s[1]; s[2] = write; s[3] = 0xAAAAAAAA; s[4] = 1; s[5] = buf; s[6] = 0xA; } int main() { function(); return 0; } |
ROP 32bit :: ROP Chain
64bit와 다르게 인자가 stack으로 전달되기 때문에, 함수를 연속해서 호출하려면 esp의 위치를 맞춰 줘야 한다. 이것은 pop [reg] ; ret gadget을 사용해 해결할 수 있다.
아래 그림은 ROP로 인자가 각각 3개, 2개인 함수 2개를 호출하는 것을 도식화한 것이다.

아래 코드는 read로 문자열을 입력받고 printf로 출력한다.
|
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> char buf[0x10]; void gadget() { __asm ( "pop %ebx\n\t" "pop %ecx\n\t" "pop %ebp\n\t" "ret\n\t" ); } void function() { uint32_t s[1]; s[2] = read; s[3] = (uint32_t)gadget + 3; s[4] = 0; s[5] = buf; s[6] = 0x10; s[7] = printf; s[8] = 0xAAAAAAAA; s[9] = "%s\n"; s[10] = buf; } int main() { function(); return 0; } |
Additional ROP Gadgets
32bit에서 gadget의 용도는 오로지 esp를 증가시키는 것이기 때문에, 항상 pop을 쓸 필요는 없다.
rp++으로 gadget 목록을 보면, 다음과 같이 add esp, 0x8 이나 add esp, 0x10 이 보인다. pop 개수가 부족하다면 esp를 증가시켜주는 gadget을 사용해 stack을 정리하는 방법을 사용할 수 있다.
|
syine@MinetaLinux:~/Desktop/test rp-lin-x86 -r 5 -f ./test | grep "add esp"
0x080492ad: add byte [eax], al ; add esp, 0x08 ; pop ebx ; ret ; (1 found) 0x080492a9: add ebx, 0x00002D57 ; add esp, 0x08 ; pop ebx ; ret ; (1 found) 0x0804901f: add esp, 0x08 ; pop ebx ; ret ; (1 found) 0x080492af: add esp, 0x08 ; pop ebx ; ret ; (1 found) 0x0804927d: add esp, 0x0C ; pop ebx ; pop esi ; pop edi ; pop ebp ; ret ; (1 found) 0x08049122: add esp, 0x10 ; leave ; ret ; (1 found) 0x0804916f: add esp, 0x10 ; leave ; ret ; (1 found) 0x0804901a: sal byte [edx+eax-0x01], 0xFFFFFFD0 ; add esp, 0x08 ; pop ebx ; ret ; (1 found) |
'Pwn > Techniques' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Linux] ptmalloc2 Heap Exploitation :: fastbin dup with consolidation (0) | 2020.06.26 |
|---|---|
| [Linux] ptmalloc2 Heap Exploitation :: fastbin corruption (0) | 2020.06.26 |
| [Linux] ptmalloc2 Heap Exploitation :: fastbin dup (0) | 2020.06.25 |
| [Linux] Return Oriented Programming (ROP) - x86 64bit (1) | 2020.05.27 |
